Horse Farrier
The foundation of every horse is healthy hooves

Horse Farrier
A horse farrier specializes in equine hoof care. This takes a combination of vet skils and blacksmithing. Trimming and balancing the hooves is important before shoeing. Horse shoes are then made to fit by heating and hammering so the horse feels balanced and no pain.

Hoof Trimming
The farrier will use large nippers to cut the excess length off and then a file to smooth the edges. Always careful not to cut too close that they bleed. They will also trim down the frog and clean the interior of the hoof well to inspect for any abscesses or injuries.

Laminitis (Foundered)
Inflammation of the lamina, (connective tissue between hoof and coffin bone) causing pain; equine walks tenderly, shifts weight to rear, doesn't want to walk at all or wants to lie down. This is a medical emergency and a vet should treat as soon as you notice it.
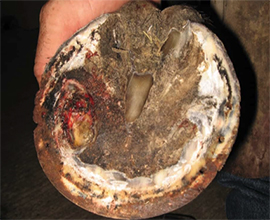
Thrush & Abscesses
Thrush is a painful bacterial infection of the frog that sells foul and dark, clay-like material surround the frog being consistently packed with manure, mud, or moist bedding. Basic hoof care includes using that hoof pick and not letting them stand in mud and manure constantly.
Hoof Care
Other diseases and conditions every equine owner should know
An infection in the soft part of the hoof may be a result of a puncture wound or injury. With an an abscess you may notice; lameness with severe pain in the affected area, a dark spot on the hoof, oozing or draining of pus and blood.
If the sole is bruised due to improper shoeing or trimming, or by rocks or other foreign objects, the equine may become lame. Corns are bruises of the sole that appear at the angle formed by the wall and bar often on the inside front feet.
There are a variety of hoof cracks including; grass cracks, sand cracks, and horizontal cracks also known as "blow-outs." A crack is a separation or break in the hoof wall and are identified according to their location as toe, quarter or heel cracks.
Navicular disease starts with inflammation and a gradual deterioration of the bony tissue of the navicular bone. Genetics, poor conformation, improper nutrition, and continuous impact of the toe against hard surfaces are the most common causes.
Quittor is a chronic, deep infection of the lateral cartilages of the coffin bone. This usually begins due to penetrating injuries to the sole or injury from being stuck by another hoof, pus,swelling, and heat will be noticeable above the coronet.
Seedy Toe disease is an infection caused by bacteria, yeast, or fungus causing the white line to disintegrate. This disease starts at the ground level and works its way up to the white line, the coronary band and can create a holow space in the hoof.
The hoof has two bulbs that contact the ground together. If one is sheared it causes the weight inside to bear on the outside heel. Improper trimming and poor conformation are the usual causes however it is serious and can lead to lameness.
Most common in front feet but can happen in all four, excessive concussion along with incorrect shoeing causes the cartilage to convert into bone. Poor conformation can be a predisposing factor. In the acute ossifying stage, pain, heat and swelling occur.
Keeping your equine sound with hoof care is your responsibility. We take it very serious at THR because we know how important a good foundation is to the overall health of an equine. Part of the physical check up will include being seen by a horse farrier.